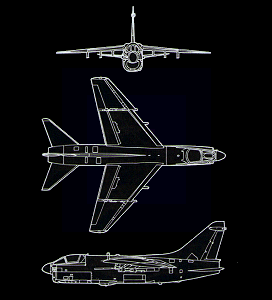
| Specifications |
| Description | | Data | |
| Developer | | Vought |
| Type | | Carrier-borne attack |
| Crew | | 1
| Power Plant | | Allison Rolls Royce TF41-A-1 turbofan |
| Wingspan | | 38.78 ft (11.8 m) |
| Length | | 46.13 ft (14.06 m) |
| Inflight refueling | | Probe and Drogue |
| Weight | | 18,942 lb (8,592 kg) |
| Radar | |
|
| Performance |
| Action | | Data |
| Ceiling | | 43,000 ft (13,106 m) |
| Max Tow / Max Lift | | 15,000 lb |
| Payload | | 15,000 lb (6,804 kg) |
| Topspeed | | |
| at sea level | 572 knots (1,060 km/h) |
| | at hight | 800 knots |
| Cruise | | 470 knots |
| Combat Radius | | 410 knot mi |
|
| Armament / Ordanace |
| Type | Size | Max | Placement |
| 6 barrel Auto-cannon | 20 mm | 300 rds | Internal right side Forward nose |
| Conventional Dumb bombs | | 15,000 lb (6,804 kg) | 1/pilon 3/pilon split |
| Inindiary or Napalm | 50 gal. canister | 4 | 1/pilon |
|